Blow molding is a manufacturing process widely used to create hollow thin-wall plastic objects such as bottles, cases, containers, and bellows.
A typical blow molding process begins with a heated hollow thermoplastic tube, also known as preform or parison. The plastic tube has a hole in one end, allowing compressed air to enter. It is then inflated into the closed chamber of a divided mold to conform to the shape of the mold cavity. The molded plastic will be left to cool and harden. Once released from the mold, the plastic part can be post-processed to have the holes rimmed or residues trimmed.
Not all plastics are suitable for blow molding. THe most frequently used materials in blow molding are
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE), High Density Polyethylene (HDPE),Polypropylene (PP),Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC),Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
The products manufactured by blow molding, although limited to hollow shaped plastics, are widely used in many industrial fields and everyday lives. The following are the products that see a lot of blow molded parts:
Automobile,Consumer,Electronics,Fuel oil tanks,Furniture,Health & safety,Lawn & garden,Marine,Medical,Packaging,Point of sale displays,Recreational,Seating
Sporting goods,Toys
There are three most popular types of blow molding:
Extrusion blow molding
Injection blow molding
Stretch blow molding
Extrusion blow molding is the oldest, simplest, and most common type of blow molding. Common gallon or larger size gas tanks and water tanks are often manufactured using extrusion blow molding. Its procedures are:
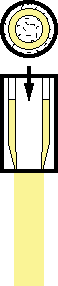 |
1.A hot hollow tube of thermoplastic material is dropped from an extruder. This tube is usually called parison. |
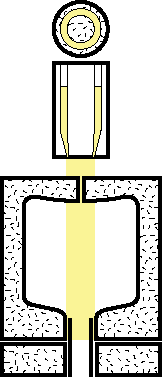 |
2.The parison is then captured in the closed chamber of a divided mold which seals one end of the parison and leaves the other end open. |
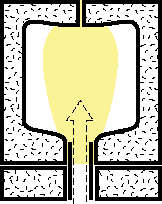 |
3.Compressed air is injected through the open end of the parison. The parison is expanded like an inflated balloon. |
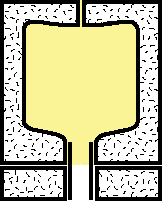 |
4.Compressed air continues to blow in until the parison reaches the wall of the mold. The hollow parison now conforms to the shape of the mold cavity. |
 |
5.The molded plastic stays in the mold until it cools and hardens. Once released from the mold, further handlings such as rimming and trimming can be performed. |
Pros and Cons of Extrusion Blow Molding
Pros
Simple,Low costs
Fast to setup to begin production
Allows a wide variety of container shapes
Can produce large size containers
Cons
Production speed is slower than other newer blow molding methods.
Not suitable for precision parts. Wall thickness is difficult to control.
Limited to hollow parts.
Injection blow molding is a process combining injection molding and blow molding. Its procedures are illustrated and described in the following table:
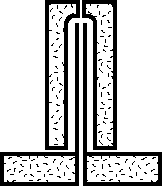 |
1.The blow stem is placed in an injection mold. |
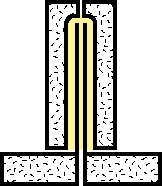 |
2.The melted thermoplastic material is injected into the injection mold and formed around the blow stem. |
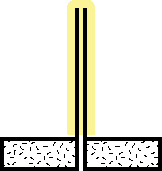 |
3.The blow stem is now wrapped with the "preform". |
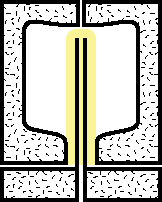 |
4.The preform along with the blow stem are then placed in the blow molding chamber. |
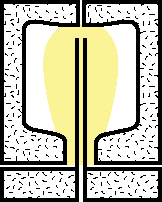 |
5.Compressed air is injected through the blow stem into the preform. The preform is expanded like an inflated balloon. |
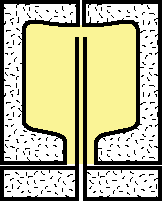 |
6.Compressed air continues to blow in until the preform reaches the wall of the mold. |
 |
7.The molded plastic stays in the mold until it cools and hardens. |
Pros and Cons of Injection Blow Molding
Pros
Faster production speed than extrusion blow molding
Higher precision than extrusion blow molding, but still not exactly a precision process
Net cost may be lower in high volume production
Cons
Higher setup costs due to two different molds.
May take longer to setup to produce the first product.
Less flexible in adjusting for different product gram weights.
Limited to hollow parts.
Limited to smaller containers.
Limited to simple shapes with no handles.
Stretch blow molding is a two-stage process similar to that of injection blow molding. First, a test-tube like preform is made using injection molding or a similar process. The neck of the preforms is fully finished but the diameter and length of the body portion are much smaller than the final product. The preform then undergos a stretch-and-blow process.
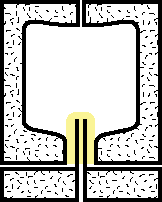 |
1.A small piece of thermoplastic material is preformed to a test-tube shape and installed near the tip of the blow stem. The setup is placed in the closed chamber of a divided mold. |
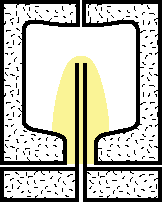 |
2.Compressed air is injected into the preform via the blow stem while the blow stem is pushing forward to stretch the preform further into the mold. |
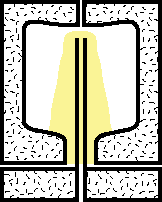 |
3.The blowing and stretching process continues. The blow stem stops near the far end of the mold. |
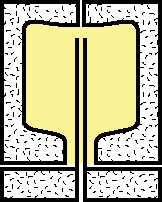 |
4.Compressed air continues to blow in until the preform reaches the wall of the mold. |
 |
5.The plastic piece is removed from the mold after it cools and hardens. |
The single most important product made by stretch blow molding is the 2-liter PET bottle for carbonated soft drinks introduced in 1978 and updated to one-piece bottle in early nineties. The PET bottles are virtually unbreakable, lightweight, transparent. They and have various (good) barrier properties. The traditional glass containers cannot compete with PET bottles and are almost extinct from the field of carbonated soft drinks.
Pros and Cons of Stretch Blow Molding
Pros
Very fast production speed
Very repeatable and stable product quality
Cons
Very high setup costs which can only be justified by extremely high production volumes (in the millions).
Will take longer to setup to produce the first product.
Less flexible in adjusting for different product gram weights.
Limited to certain plastic materials, such as PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate).
Limited to hollow parts.
Limited to smaller containers.
Limitedd to simple shapes with no handles.

